Humans need oxygen to breathe properly and without it, the cells would not be able to respire. However, there are some health conditions that result in people being unable to breathe in as much oxygen as they need.
Usually, this is because the lungs become less efficient or less functional. Depending on the disease, this might be due to reducing lung capacity or a build-up of mucus in the lungs.
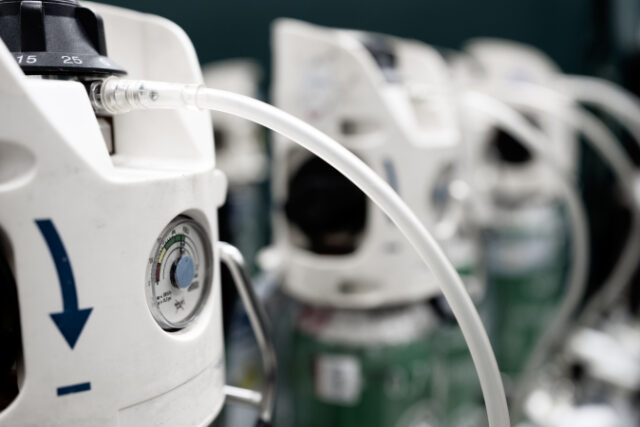
When the lungs aren’t functioning optimally, oxygen therapy might be required. Oxygen therapy provides supplemental oxygen to the individual who is affected.
What Are the Methods for Oxygen Therapy?
There are a few different methods of oxygen supplementation in oxygen therapy, including the use of:
- Tubes – the first port of call is a nasal cannula, which is two small, flexible tubes that get placed by the ends of the nostrils. The cannula is attached to an oxygen tank and it supplies regular oxygen to help the individual breathe.
- Face masks – the next option is a face mask, which is used when nasal tubes are unsuitable. Face masks cover the nose and mouth and can supply a higher amount of oxygen to the individual.
- Surgery – in serious cases, surgery might be required to create a hole in the trachea. A tube can be placed directly into the hole to provide ongoing oxygen. This is known medically as transtracheal therapy.
Oxygen can be delivered in a few different ways, including as a gas or liquid, or via hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Both gas and liquid oxygen can be stored in an oxygen tank that can be taken home by the patient if needed.
Smaller oxygen tanks usually deliver the oxygen in pulses to make the supply last as long as possible. If the tank is filled with liquid oxygen, it provides a larger oxygen supply. For this reason, somebody who is more active might be offered liquid oxygen over gas oxygen.
The best portable oxygen concentrators take oxygen from the air in the room and concentrate it to a therapeutic level. Oxygen concentrators remove other gases that are found naturally in the air to supply concentrated oxygen to the patient.
Oxygen concentrators are more cost-effective and don’t require refills since they pull oxygen from the air to function. They are appropriate for most people, whether they’re using nasal tubes, face masks, or a trans tracheal tube.
Some patients will qualify for hyperbaric oxygen therapy, which uses pure oxygen in a pressurized room. Inside the room, the air pressure reaches 3-4 times its normal levels.
With the high concentration of oxygen, the gas can get delivered quickly to the tissues and organs of the body. It’s often used in the treatment of infections, wounds, or air bubbles in the blood.
Which Lung Health Conditions Require Oxygen Therapy?
Oxygen therapy can be prescribed for anybody who is unable to get enough oxygen through their lungs naturally. There is a range of health conditions that might reduce oxygen absorption in the lungs, including:
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Pneumonia
- Asthma
- Cystic fibrosis
- Lung disease
- Sleep apnea
- Bronchopulmonary dysplasia
- Lung trauma or injury
- Reduced lung capacity due to lung cancer
Measuring Blood Oxygen Levels
Doctors will use a range of methods to measure the amount of oxygen in the blood to determine whether somebody qualifies for oxygen therapy. They can measure the levels of oxygen in the arterial blood directly by taking a blood sample.
Alternatively, they can use an oxygen saturation monitor. A pulse oximeter gets clipped onto the end of a finger or toe and measures the levels of oxygen saturation in their blood.
Normal arterial blood oxygen levels lie between 75 and 100 mmHg. If the oxygen levels fall below 60 mmHg, the individual might be offered oxygen therapy.
It’s important for doctors to monitor the levels of oxygen in the blood before and during oxygen therapy to prevent over-saturation. More isn’t always better.
Oxygen levels should not exceed 110 mmHg. Too much oxygen can be dangerous for the body, and it can damage to lungs.
To prevent over-saturation with oxygen, some people might only require occasional oxygen supplementation. Others might need to more often and will be offered a portable oxygen tank to take home with them.
What Are the Symptoms of Low Oxygen Levels?
The symptoms of low oxygen are:
- Breathlessness
- Increased heart rate
- Rapid breathing
- Wheezing
- Coughing
- Excessive sweating
- Confusion
- Blue tinge to the skin
If you experience any of the above symptoms, you just seek medical attention immediately. Low oxygen levels can be very damaging to the brain and body. The damage can worsen over time if you continue to have an inadequate amount of oxygen in your body.
What Are the Benefits of Oxygen Therapy?
Oxygen therapy is essential for some people, especially if their lung function is severely impaired. Otherwise, they are at risk of suboptimal oxygen levels. For others, oxygen therapy isn’t a necessity but it can be beneficial at regular intervals.
Here are some of the benefits of using supplemental oxygen:
- Easier to exercise
- Increased energy
- Elevated mood
- Reduced headaches
- Reduced swelling
- Improved sex
- Reduced risk of heart failure
- Improved quality of life
- Extended lifespan
What Are the Complications Associated With Oxygen Therapy?
Complications can be of particular concern when patients are taking oxygen concentrators and tanks home to use without supervision. The issues arise when the patient’s oxygen levels exceed the safe range.
Patients who are given portable oxygen tanks to take home are given thorough guidance on how to use the oxygen.
Some of the important precautions include:
- Stay away from open flames when using the oxygen tank
- Do not smoke near the oxygen tank
- Don’t take your oxygen tank into confined spaces
Some people get dryness around the cannula insertion when using a nasal tube. The skin can become irritated due to the cannula rubbing on the area as the person moves around.
Nosebleeds and headaches aren’t uncommon. However, patients are advised to inform their doctor if they experience the onset of severe symptoms.